Vaccinated vs. Unvaccinated: Serious and Irreversible Neurological, Developmental, and Immune-Related Health Risks
Four Studies Reveal the Grave Consequences of Childhood Hyper-Vaccination
by Nicolas Hulscher, MPH
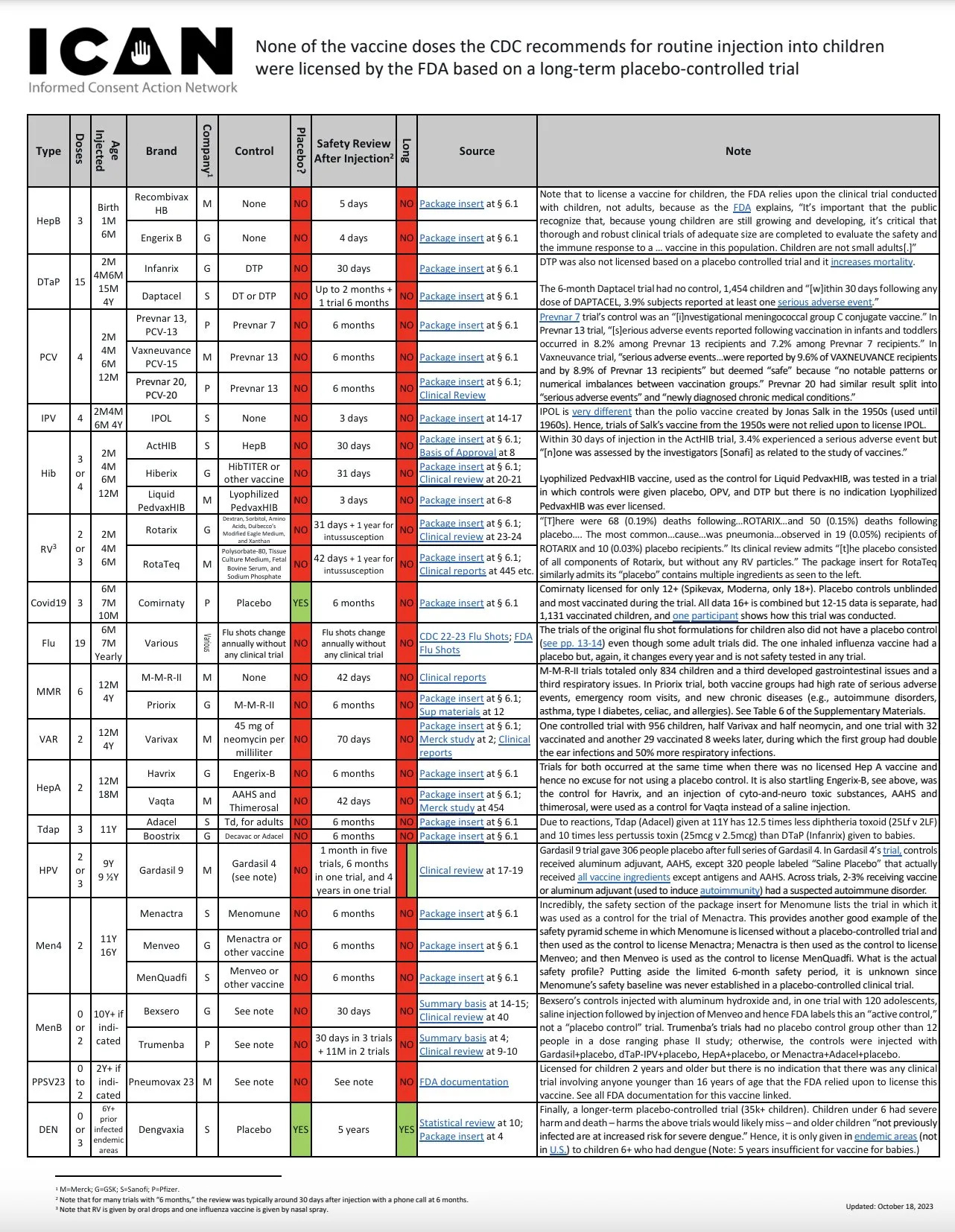
When studies compare vaccinated to unvaccinated children, they find serious and irreversible neurological, developmental, and immune-related health risks. This is likely one of the primary reasons that prevents Big Pharma and our regulatory agencies from conducting such studies — their flawed business model of pushing inadequately tested injections would collapse as parents learn the true risks of vaccination. It’s important to remember that ALL of the routine childhood vaccines were licensed WITHOUT proper long-term, placebo-controlled trials:
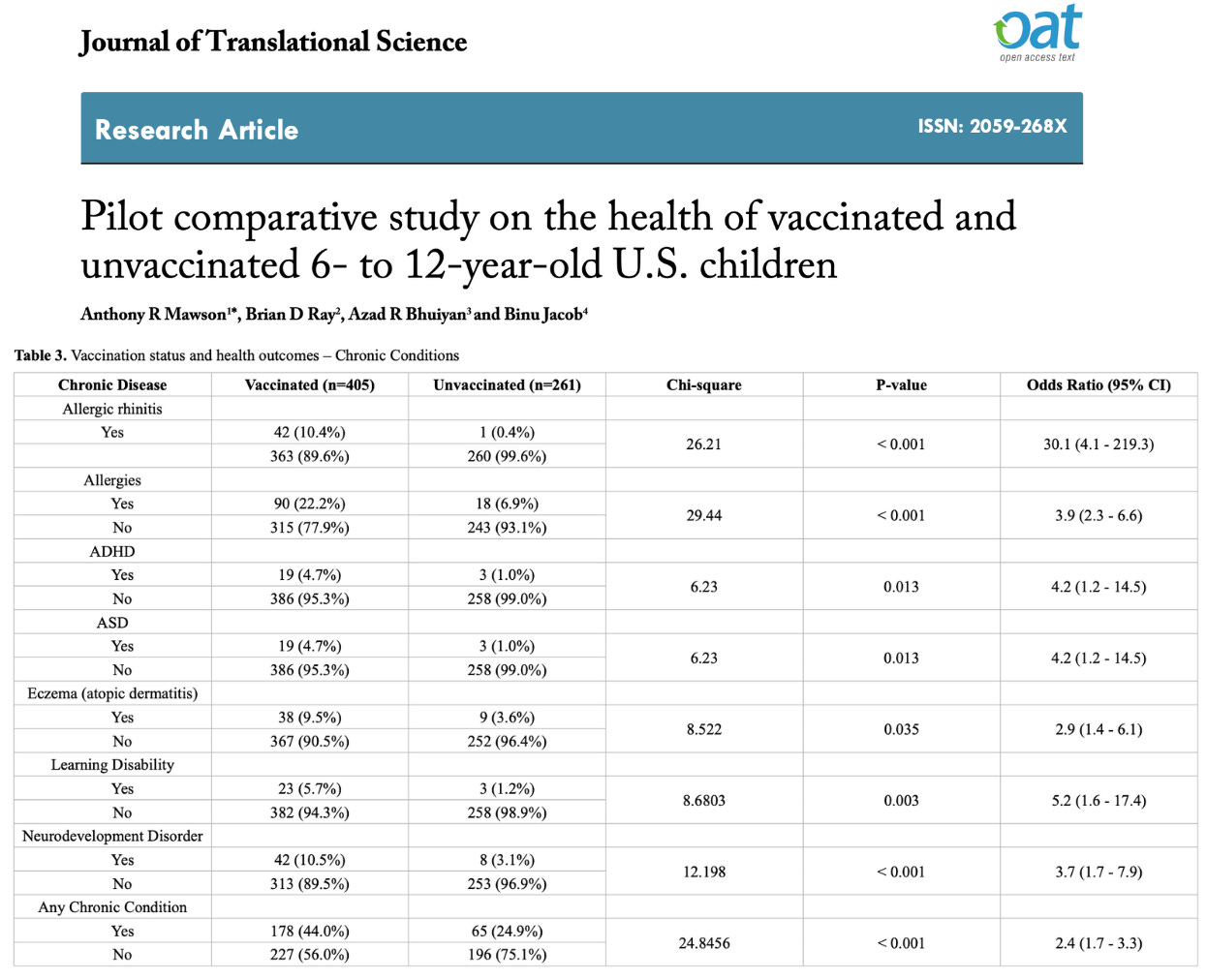
Mawson et al (2017)
N = 666 homeschool children (39% unvaccinated)
Design: Cross-sectional study via anonymous online survey of homeschool mothers in four U.S. states (FL, LA, MS, OR)
Data Collected: Vaccination status, physician-diagnosed illnesses, medication use, and health services
Analysis: Chi-square tests, odds ratios, and logistic regression
Key Findings – Increased Risks in Vaccinated Children
Overall Increased Risks
Any chronic illness: OR 2.4 (140% increased risk, p < 0.001)
Any neurodevelopmental disorder (NDD – learning disability, ADHD, or ASD): OR 3.7 (270% increased risk, p < 0.001)
Vaccinated preterm children & NDD: OR 6.6 (560% increased risk, p < 0.001)
Neurodevelopmental Disorders (NDDs)
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): OR 4.2 (320% increased risk, p = 0.013)
Learning disability: OR 5.2 (420% increased risk, p = 0.003)
ADHD: OR 4.2 (320% increased risk, p = 0.013)
Chronic Illnesses
Allergic rhinitis: OR 30.1 (2,910% increased risk, p < 0.001)
Other allergies: OR 3.9 (290% increased risk, p < 0.001)
Eczema (atopic dermatitis): OR 2.9 (190% increased risk, p = 0.035)
Acute Respiratory & Ear Infections
Otitis media (ear infections): OR 3.8 (280% increased risk, p < 0.001)
Pneumonia: OR 5.9 (490% increased risk, p = 0.001)
Medical Interventions & Medication Use
Antibiotic use (past 12 months): OR 2.4 (140% increased risk, p < 0.001)
Allergy medication use: OR 21.5 (2,050% increased risk, p < 0.001)
Fever medication use: OR 4.6 (360% increased risk, p < 0.001)
Doctor visits for illness (past year): OR 3.0 (200% increased risk, p < 0.001)
Hospitalization (one or more nights): OR 1.8 (80% increased risk, p = 0.012)
Ventilation ear tubes: OR 8.0 (700% increased risk, p = 0.018)
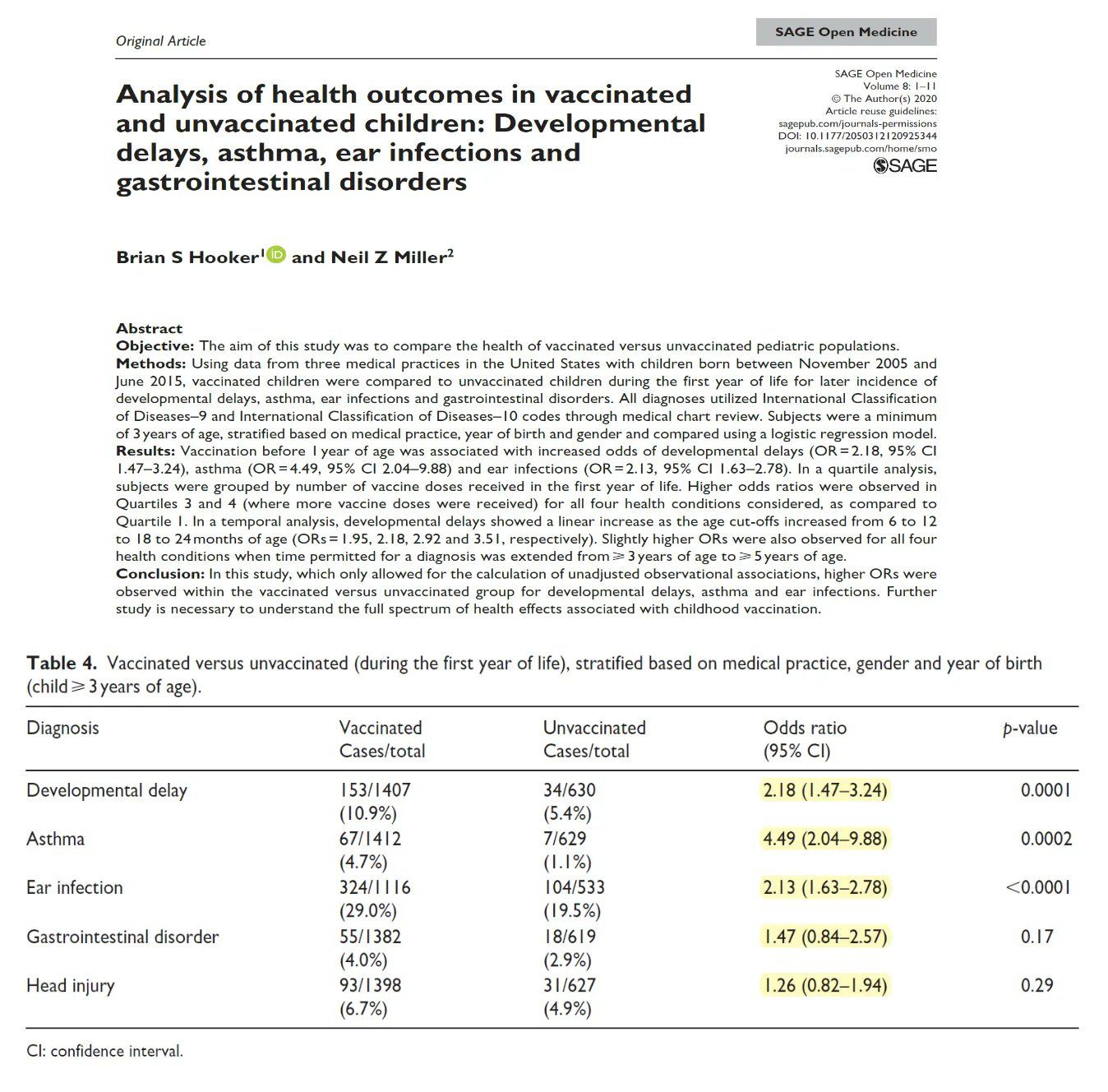
Hooker and Miller (2020)
N = 2,047 children (52% male), with 30.9% unvaccinated by age 1.
Design: Cohort study using electronic medical records (EMRs) from three pediatric medical practices in the U.S.
Data Collected: Vaccination status (vaccinated before 1 year vs. unvaccinated), physician-diagnosed conditions (ICD-9/ICD-10 codes).
Analysis: Conditional logistic regression stratified by medical practice, birth year, and gender; odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CI), p-values < 0.05 considered significant.
Key Findings – Increased Risks in Vaccinated Children
Developmental Delays
Overall developmental delay: OR 2.18 (118% increased risk, p = 0.0001)
Developmental delay in females: OR 3.10 (210% increased risk, p = 0.0068)
Developmental delay in males: OR 1.92 (92% increased risk, p = 0.0054)
Increasing risk with older age cut-offs:
6 months: OR 1.95 (95% increased risk)
12 months: OR 2.18 (118% increased risk)
18 months: OR 2.92 (192% increased risk)
24 months: OR 3.51 (251% increased risk)
Asthma & Respiratory Conditions
Asthma (overall): OR 4.49 (349% increased risk, p = 0.0002)
Asthma in males: OR 6.89 (589% increased risk, p = 0.0015)
Asthma diagnosed after 5 years: OR 4.93 (393% increased risk, p = 0.0026)
Ear Infections
Overall ear infection risk: OR 2.13 (113% increased risk, p < 0.0001)
Ear infections in females: OR 2.20 (120% increased risk, p < 0.0001)
Ear infections in males: OR 2.07 (107% increased risk, p < 0.0001)
Ear infections diagnosed after 5 years: OR 2.49 (149% increased risk, p < 0.0001)
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Overall gastrointestinal disorder risk: Not statistically significant (p = 0.17)
Gastrointestinal disorder in highest vaccine dose quartile: OR 4.03 (303% increased risk, p = 0.003)
Gastrointestinal disorder diagnosed after 5 years: OR 2.48 (148% increased risk, p = 0.045)
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Courageous Discourse™ with Dr. Peter McCullough & John Leake to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.