Health Risks from Los Angeles Wildfire Smoke: Quantifying Hospitalizations and Mortality
As Los Angeles faces its most devastating wildfires in recorded history, the health consequences of inhaling toxic smoke demand urgent attention.
by Nicolas Hulscher, MPH
As Los Angeles suffers from their most devastating wildfires in recorded history, it’s important to understand the health risks associated with inhaling wildfire smoke.
Last year, a comprehensive meta-analysis titled, Health Effects of Wildfire Smoke Exposure, was published in Annual Review of Medicine:
Here are the key findings:
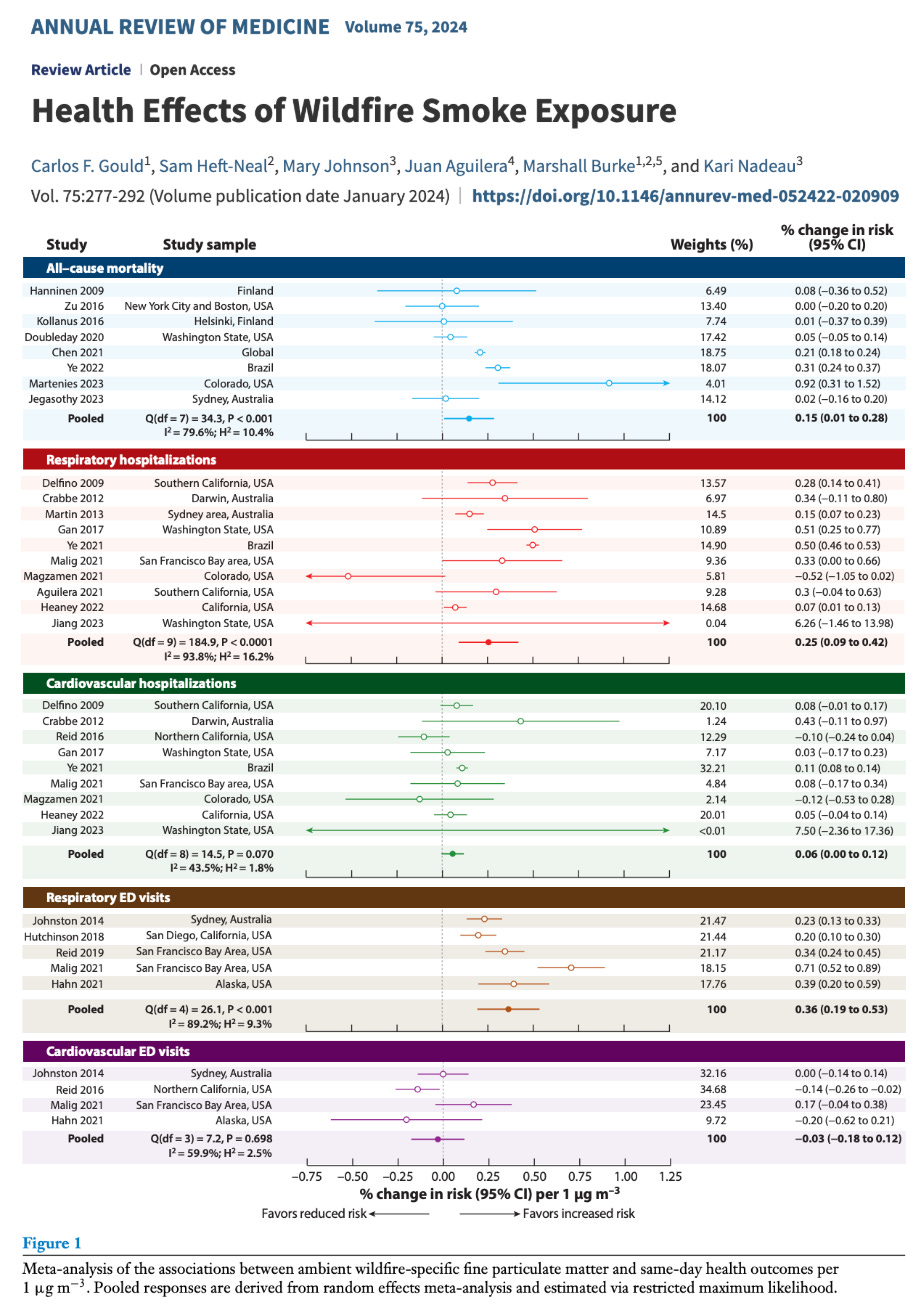
Key Health Risks from Wildfire Smoke Exposure (Same-Day Impacts)
Respiratory-Related Emergency Department (ED) Visits:
Increase: 0.36% per 1 µg/m³ of wildfire-specific PM2.5 (fine particulate matter).
Explanation: Same-day visits to emergency rooms for respiratory issues (like asthma attacks or shortness of breath) rise significantly even with small increases in smoke pollution.
Respiratory-Related Hospitalizations:
Increase: 0.25% per 1 µg/m³ of wildfire-specific PM2.5.
Explanation: Hospital admissions for breathing difficulties also increase on the same day as exposure to wildfire smoke. This affects those with chronic lung diseases such as asthma, COPD, or other respiratory infections.
Cardiovascular-Related Emergency Department (ED) Visits:
Change: No statistically significant increase observed on the same day. The study found a non-significant decrease of −0.03% per 1 µg/m³ of wildfire-specific PM2.5.
Explanation: While cardiovascular ED visits show no consistent increase on the same day, longer-term effects or other contextual factors may play a role.
Cardiovascular-Related Hospitalizations:
Increase: 0.06% per 1 µg/m³ of wildfire-specific PM2.5.
Explanation: Though smaller, this reflects an increased risk of same-day hospital admissions for heart-related issues, such as heart attacks or other cardiovascular events.
All-Cause Mortality (Deaths):
Increase: 0.15% per 1 µg/m³ of wildfire-specific PM2.5.
Explanation: Same-day exposure to wildfire smoke results in more deaths, particularly among vulnerable populations such as older adults, those with pre-existing health conditions, or those living in areas with repeated wildfire events.
Context of Current Wildfires
Next, I will use the findings from this meta-analysis to quantify possible impacts of the current wildfires. The ongoing historic wildfires are significantly impacting air quality across affected regions, with areas experiencing AQI levels ranging from 150 ("Unhealthy") to over 500 ("Hazardous"). These levels correspond to PM2.5 concentrations of approximately 55 µg/m³ (AQI 150) and 250 µg/m³ or higher (AQI > 500), respectively. Both levels represent serious health risks, with extreme consequences in high AQI zones.
AQI 150 Zones ("Unhealthy")
Based on a meta-analysis of wildfire smoke exposure (Annual Review of Medicine, 2024), these increases were calculated using the observed risk per 1 µg/m³ of wildfire-specific PM2.5. AQI 150 corresponds to approximately 55 µg/m³ PM2.5:
Respiratory Emergency Department (ED) Visits:
19.8% increase (55 × 0.36% per µg/m³ = 19.8%).Respiratory Hospitalizations:
13.75% increase (55 × 0.25% per µg/m³ = 13.75%).All-Cause Mortality (Deaths):
8.25% increase (55 × 0.15% per µg/m³ = 8.25%).Cardiovascular Hospitalizations:
3.3% increase (55 × 0.06% per µg/m³ = 3.3%).
High-Risk AQI > 500 Zones ("Hazardous")
Using the same methodology, AQI > 500 corresponds to approximately 250 µg/m³ PM2.5:
Respiratory Emergency Department (ED) Visits:
90% increase (250 × 0.36% per µg/m³ = 90%).Respiratory Hospitalizations:
62.5% increase (250 × 0.25% per µg/m³ = 62.5%).All-Cause Mortality (Deaths):
37.5% increase (250 × 0.15% per µg/m³ = 37.5%).Cardiovascular Hospitalizations:
15% increase (250 × 0.06% per µg/m³ = 15%).
It’s clear that the population health impacts of major wildfires are very significant. This is why it’s very important to take preventative measures:
In AQI 150 Zones:
Avoid outdoor activities; stay indoors with windows sealed.
Use air purifiers and wear N95/KN95 masks outdoors.
In AQI > 500 Zones:
Avoid all outdoor exposure entirely.
Seek clean air shelters or evacuate to areas with better air quality.
Clearly, California and local governments have miserably failed in wildfire prevention, leading to widespread economic destruction and significant population harm. Like Lahaina, LA was warned in 2018:
Nicolas Hulscher, MPH
Epidemiologist and Foundation Administrator, McCullough Foundation
www.mcculloughfnd.org
Please consider following both the McCullough Foundation and my personal account on X (formerly Twitter) for further content.







One must wonder if this involved any arson, also.
“What ignited the fires that burned metals and plastics, superheated CMU blocks and brick, melted cars?
“If not a wildfire, then what was the fuel that flash-lit the fires to burn across different mediums and materials?” asks James Grundvig, writing for American Media Periscope.
The first answer is all that geoengineering that has been taking place across LA for at least a decade, turning the island’s skies from crystal blue with perhaps a few puffy clouds and rain every now and again into a persistent white haze?
Heavy winds alone were not enough to spark the LA fires and cause them to consume some 5000 structures and kill many people.
Where have we heard this before?
"The water wasn’t on. Fire hydrants were dry. And the Deputy Director of Water Resource Management, who was named an Obama Foundation Leader, refused to release water for the west Maui fires until it was too late."
There also had to be fuel, and lots of it, which came in the form of chemtrail aerosols and ammonium nitrate.
By using ammonium nitrate as an oxygenating accelerant, the LA fires were able to burn cars and steel while leaving trees alone?
Known scientifically as NH4NO3, ammonium nitrate by itself is not flammable nor can it combust all on its own. What makes an NH4NO3-fueled fire unique is that instead of glowing red or some other typical color associated with a wildfire, it burns light and white. Even the sparsely present trees across that part of the island would not have constituted nearly enough fuel to cause the car-incinerating, white dust-creating infernos .
White-hot LA fires fueled by chemtrail aerosols, ammonium nitrate, warns analyst.
“Ammonium nitrate is an oxidizer; it supports the combustion of other materials,” Heavy winds alone were not enough to spark the LA fires and cause them to consume some 5000 structures and kill many people.
Even the sparsely present trees across that part of the LA would not have constituted nearly enough fuel to cause the car-incinerating, white dust-creating infernos that left LA completely devastated and basically no more.
That haze, we now know, is composed of three main chemical substances: barium (Ba), aluminum (Al), and strontium-90 (90Sr), the latter being a radioactive isotope. By using ammonium nitrate as an oxygenating accelerant for fires.
The other apparent ingredient in the LA fires is ammonium nitrate, several tons of which conveniently and mysteriously went missing off a freight train in California back on May 30.
********
Past examples:
Maui Wildfires and the Theft of Sacred Hawaiian Land
Aside from the federal government’s bureaucratic failure, Hawaiians have good reason to be suspicious of the recent fires.
"Local residents have been reporting bright flashes of light. One was captured by a home security camera that appears to have been the start of the Olinda fire.
Many people are saying that it was Directed Energy Weapons. We know that most major governments already have them. And during the California fires, online weather maps recorded what looks like a laser from above striking an area just before it bursts into flames.
In his research, Denis Mills discovered that the incendiary aluminum and barium nanodust from chemtrails is most likely fueling the ferocity of today’s so-called super wildfires. And on the day before the Maui fires broke out, locals were reporting a heavy overcast from chem-trailing that they’d never seen before.
It’s also interesting to note that the Maui police chief was the incident commander for the Las Vegas mass shooting in 2017."
https://gregreese.substack.com/p/maui-wildfires-and-the-theft-of-sacred?utm_source=substack&utm_medium=email#play